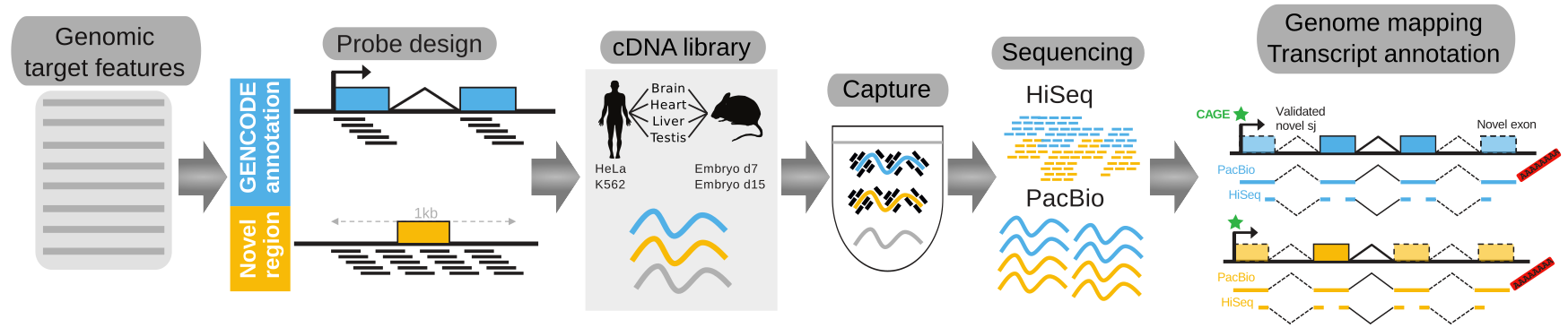
Welcome to the companion website of our GENCODE lincRNA Capture Long-Seq study (Lagarde et al., "High-throughput annotation of full-length long non-coding RNAs with Capture Long-Read Sequencing", Nature Genetics, 2017).
The aim of this site is to enable easy navigation and download of the various datasets and software related to this project.
Summary
Accurate annotations of genes and their transcripts is a foundation of genomics, but no annotation technique presently combines throughput and accuracy. As a result, reference gene collections remain incomplete: many gene models are fragmentary, while thousands more remain uncatalogued - particularly for long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs). To accelerate lncRNA annotation, the GENCODE consortium has developed RNA Capture Long Seq (CLS), combining targeted RNA capture with third-generation long-read sequencing (PacBio). We present an experimental re-annotation of the GENCODE intergenic lncRNA population in matched human and mouse tissues, resulting in novel transcript models for 3,574 / 561 gene loci, respectively. CLS approximately doubles the annotated complexity of targeted loci, outperforming existing short-read techniques. Full-length transcript models produced by CLS enable us to definitively characterize the genomic features of lncRNAs, including promoter- and gene-structure, and protein-coding potential. Thus CLS removes a longstanding bottleneck of transcriptome annotation, generating manual-quality full-length transcript models at high-throughput scales.
Supplementary Data
All genome-mapped data are based on versions GRCh38 (a.k.a. hg38, human) and GRCm38 (a.k.a. mm10, mouse).
In addition to the files mentioned in this section, raw (FASTQ files) and processed files (BED files of capture probes and merged transcript models) are available from the GEO database under accession GSE93848.
Track Hub
The GENCODE CLS Track Hub can be loaded directly into the UCSC Genome Browser using these links:
Merged Transcript Models
Transcript models were built from HCGMsHigh-Confidence Genome Mappings are PacBio read alignments with the following characteristics:
- Uniquely mapped
- Double-bounded: the read contains both library adapters (i.e., its cDNA insert is believed to be fully sequenced)
- If spliced, its constituting introns must all be canonical (GT|GC/AG)
- If unspliced, it must bear a detectable polyA tail using two distinct approaches, "anchored" and "standard/non-anchored". Each method has its own pros and cons:
-
The "anchored" procedure prevents the transcripts whose end(s) are supported by CAGE or polyA data from being merged into a longer, compatible transcript "container". This preserves all supported transcript ends in the output, including internal sites. It’s also the set analyzed in the paper. On the other hand, many distinct models of this set differ only by their TSS/TTS, i.e., it contains many redundant intron chains.
-
The "standard/non-anchored" approach produces merged transcript models the same way GENCODE, or standard merging software (e.g. Cuffmerge), do. This means that all transcripts with compatible intron chains are considered redundant, and thus merged into a single "container", regardless of their end support. Its main disadvantage is that it discards many alternative, internal TSSs/TTSs in the process. On the plus side, this procedure guarantees that intron chains are totally non-redundant in the merged set.
"Anchored" method
-
GTF files are listed here.
-
Equivalent BED files are available from GEO.
-
Transcript-to-biotype assignments are listed here. These files also contain the identifiers of the genomic features overlapped (mostly GENCODE gene_ids) by each transcript structure.
-
Transcripts with HiSeq-supported splice junctions are listed here (contains also mono-exonic transcript models).
Standard method (non-anchored)
-
GTF files are listed here.
-
Transcript-to-biotype assignments are listed here. These files also contain the identifiers of the genomic features overlapped (mostly GENCODE gene_ids) by each transcript structure.
-
Transcripts with HiSeq-supported splice junctions are listed here (contains also mono-exonic transcript models).
"GENCODE+" lncRNA annotations
GENCODE+ consists in the union of GENCODE and CLS lncRNAs.
Read alignments
Post-capture only.
Raw BAM files
Listed in this directory. These files correspond to the ones loaded into the project’s Track Hub.
Warning: these alignments are unstranded. See below for a stranded version.
Processed PacBio read alignments (HCGMsHigh-Confidence Genome Mappings are PacBio read alignments with the following characteristics:
- Uniquely mapped
- Double-bounded: the read contains both library adapters (i.e., its cDNA insert is believed to be fully sequenced)
- If spliced, its constituting introns must all be canonical (GT|GC/AG)
- If unspliced, it must bear a detectable polyA tail)
Listed in this directory (in GTF format).
Each read alignment is stranded according to its intron motifs and polyA tail location (see Methods section of the paper for more details).
Read biotypes
PacBio read-to-biotype assignments are listed here (HCGMsHigh-Confidence Genome Mappings are PacBio read alignments with the following characteristics:
- Uniquely mapped
- Double-bounded: the read contains both library adapters (i.e., its cDNA insert is believed to be fully sequenced)
- If spliced, its constituting introns must all be canonical (GT|GC/AG)
- If unspliced, it must bear a detectable polyA tail only). These files also contain the identifiers of the genomic features overlapped (mostly GENCODE gene_ids) by each read.
Transcription Start Sites
Transcription Start Sites (TSSs) derived from HCGMsHigh-Confidence Genome Mappings are PacBio read alignments with the following characteristics:
- Uniquely mapped
- Double-bounded: the read contains both library adapters (i.e., its cDNA insert is believed to be fully sequenced)
- If spliced, its constituting introns must all be canonical (GT|GC/AG)
- If unspliced, it must bear a detectable polyA tail are available in two flavors:
Raw TSSs
These BED files contain the coordinates of all raw TSSs called using HCGMsHigh-Confidence Genome Mappings are PacBio read alignments with the following characteristics:
- Uniquely mapped
- Double-bounded: the read contains both library adapters (i.e., its cDNA insert is believed to be fully sequenced)
- If spliced, its constituting introns must all be canonical (GT|GC/AG)
- If unspliced, it must bear a detectable polyA tail. The corresponding PacBio reads are also identified.
Clustered TSSs
These BED files contain the coordinates of all merged TSSs (one record per non-redundant TSS). The PacBio reads contributing to each site are also identified.
Clustered TSSs split by known / novel status (with respect to GENCODE) are available in this directory.
PolyA reads, sites and signals
Raw sites
These BED files contain the coordinates of all raw polyA sites called using captured PacBio reads. The corresponding poly-adenylated PacBio reads are also identified.
Clustered sites
These BED files contain the coordinates of all merged polyA sites (one record per non-redundant polyA site). The poly-adenylated PacBio reads contributing to each site are also identified.
PolyA signals
The sequences and genome coordinates of putative polyA signals used in the study are available here.
Splice junctions
PacBio canonical Splice Junctions (SJs) are available here (in GTF format). They were derived from the PacBio read mappings available here.
Analysis of splicing motifs
We ran geneid to score various sets of splice sites using this parameter file. The resulting sets are linked below:
Software
-
samToPolyA: Calls poly-adenylated reads and polyA sites from read alignments. -
matchDistribution: Given distinct "subject" (S) and a "target" (T) distributions, attempts to mimic T’s density (i.e., its shape) by sampling from S’s population. Used in this project to expression-match sets of protein-coding TSSs to lncRNA ones. -
anchorTranscriptsEnds: prepare a GTF file of mapped transcriptome reads for anchored transcript merging. -
compmerge: used to merge the HCGMsHigh-Confidence Genome Mappings are PacBio read alignments with the following characteristics:
- Uniquely mapped
- Double-bounded: the read contains both library adapters (i.e., its cDNA insert is believed to be fully sequenced)
- If spliced, its constituting introns must all be canonical (GT|GC/AG)
- If unspliced, it must bear a detectable polyA tail into a non-redundant set of transcript models. -
IPSA(Integrative Pipeline for Splicing Analyses), used to extract splice junctions and their read counts from alignments of Illumina HiSeq data. -
comptr: compare a set of transcripts to a reference annotation.